
When it comes to financial planning, life insurance and life assurance play pivotal roles in safeguarding our future. However, the terms “assurance” and “insurance” are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion. Understanding the key differences between these two concepts is crucial for making informed decisions. Knowclick Media delves into the distinctions, benefits, and implications of assurance and insurance, helping you choose the best policy for your needs.
What is Life Assurance?
Assurance is a financial product that provides a payout in the event of a certain event, such as death. It is a form of long-term financial protection designed to offer peace of mind and financial security to beneficiaries. Assurance policies are typically whole life policies, meaning they cover the policyholder for their entire life.
Key Features of Life Assurance:
- Lifetime Coverage: Assurance policies are designed to last for the policyholder’s lifetime.
- Guaranteed Payout: Beneficiaries receive a guaranteed payout upon the policyholder’s death.
- Premiums: Premiums are usually higher and can be paid throughout the policyholder’s life or for a limited period.
- Investment Component: Many assurance policies have an investment component, allowing the policy to accumulate cash value over time.
- Policy Loans: Policyholders can often take loans against the cash value of the assurance policy.
What is Life Insurance?
Insurance, on the other hand, is a financial product that provides protection against specific risks for a defined period. It typically involves paying regular premiums to receive coverage for unexpected events such as accidents, illness, or death within the term of the policy.
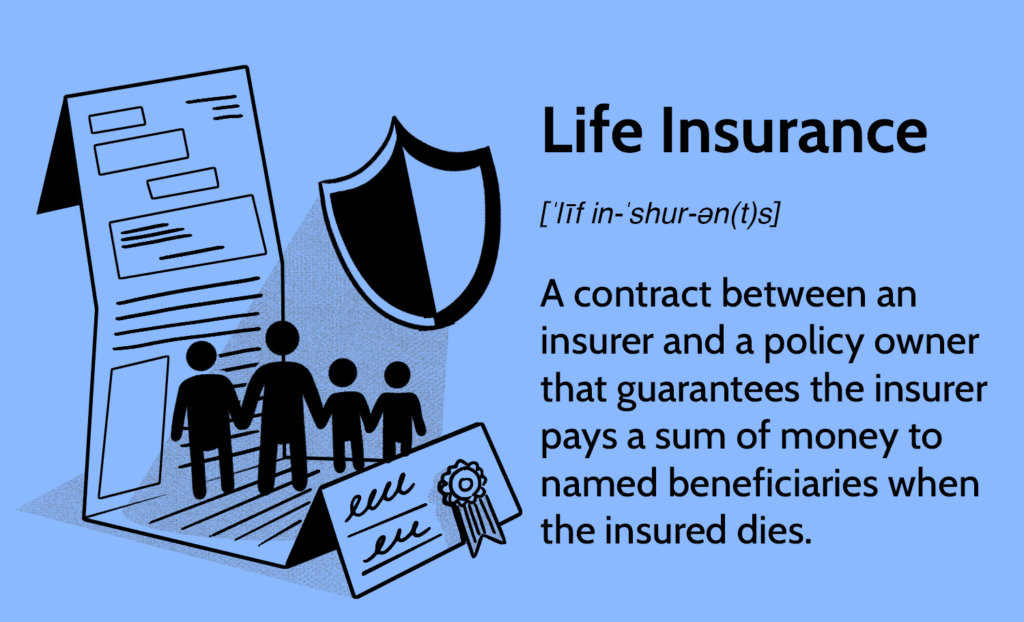
Key Features of Insurance:
- Fixed Term: Insurance policies are usually for a specified term, such as 10, 20, or 30 years.
- Conditional Payout: Payouts are made only if the specified event (e.g., death) occurs during the policy term.
- Lower Premiums: Premiums are generally lower compared to assurance policies because the coverage is temporary.
- No Investment Component: Insurance policies typically do not accumulate cash value.
- Renewability: Policies can often be renewed or converted to permanent insurance.
Types of Life Assurance and Insurance Policies
Life Assurance:
- Whole Life Assurance: Provides coverage for the policyholder’s entire life with a guaranteed payout upon death.
- Endowment Assurance: Combines life assurance with savings, providing a payout either upon death or at the end of a specified term.
Life Insurance:
- Term Life Insurance: Offers coverage for a specific term, paying out only if the policyholder dies within that period.
- Whole Life Insurance: Similar to whole life assurance, providing lifelong coverage with a guaranteed payout.
- Universal Life Insurance: A flexible policy with adjustable premiums and death benefits, often including an investment component.
Financial Benefits of Life Assurance and Insurance
Assurance:
- Long-term Security: Assurance policies ensure that beneficiaries receive financial support regardless of when the policyholder passes away.
- Cash Value Accumulation: Policies with an investment component can build significant cash value, which can be used for loans or as a financial cushion.
- Estate Planning: Assurance can be a crucial part of estate planning, providing funds to cover estate taxes or debts.
Insurance:
- Affordable Coverage: Term insurance offers a cost-effective way to get substantial coverage for a fixed period.
- Flexibility: Insurance policies can be tailored to cover various risks and time frames, making them versatile for different financial needs.
- Temporary Needs: Ideal for covering temporary financial obligations, such as mortgage payments or children’s education costs.
Risk Management in Life Assurance and Life Insurance
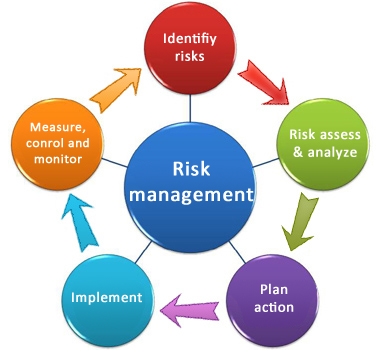
Both assurance and insurance serve as tools for managing financial risks. However, the approach to risk management differs between the two:
Life Assurance:
- Certainty: Provides a guaranteed benefit, ensuring that financial risks associated with death are covered.
- Investment Risks: With the investment component, there’s a potential for growth, but also some exposure to market risks.
Insurance:
- Specific Risks: Focuses on covering specific, often temporary, risks such as accidental death or critical illness.
- Renewability Risks: The risk of increased premiums or denial of coverage upon renewal can be a consideration for policyholders.
Policyholder Rights in Life Assurance and Life Insurance
Understanding your rights as a policyholder is crucial for managing your policy effectively.
Life Assurance Policyholder Rights:
- Access to Cash Value: Policyholders can access the accumulated cash value through loans or withdrawals.
- Policy Surrender: Policyholders can surrender their assurance policy for its cash value, although this may incur penalties.
- Beneficiary Designation: Policyholders can designate and change beneficiaries as needed.
Insurance Policyholder Rights:
- Policy Renewal: Policyholders typically have the right to renew their term insurance policies, though terms may vary.
- Conversion Options: Many term policies offer options to convert to permanent insurance without a medical exam.
- Claim Filing: Policyholders or beneficiaries have the right to file claims in the event of the covered incident occurring.
Claim Processes for Assurance and Insurance
The claim process can vary significantly between assurance and insurance policies. Understanding these processes ensures a smoother experience during challenging times.
Life Assurance Claim Process:
- Notification: Beneficiaries notify the insurance company of the policyholder’s death.
- Documentation: Provide necessary documentation, such as the death certificate and policy details.
- Verification: The insurance company verifies the claim and processes the payout.
- Payout: Beneficiaries receive the guaranteed payout, typically as a lump sum.
Insurance Claim Process:
- Incident Report: Notify the insurance company of the incident (e.g., death, illness).
- Submit Proof: Submit required proof, such as medical records or death certificates.
- Investigation: The insurer investigates the claim to ensure it meets the policy terms.
- Decision: The insurer approves or denies the claim based on their findings.
- Payout: If approved, the payout is made according to the policy terms, either as a lump sum or in installments.
Regulatory Framework for Assurance and Insurance
Both assurance and insurance are regulated to protect policyholders and ensure fair practices. Understanding the regulatory framework helps in selecting reputable insurers and comprehending policy terms.
Life Assurance Regulation:
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA): Regulates assurance policies to ensure fair practices and financial stability of insurers.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Protect policyholders from unfair practices and ensure transparency in policy terms.
Insurance Regulation:
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): Sets standards and regulations for insurance policies, promoting uniformity and consumer protection.
- State Insurance Departments: Each state has its own regulatory body overseeing insurance practices within its jurisdiction.
- Solvency Regulations: Ensure that insurers maintain adequate reserves to pay claims and remain financially solvent.
Choosing Between Assurance and Insurance
Deciding between assurance and insurance depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and long-term plans.
Consider Assurance If:
- You want lifetime coverage with a guaranteed payout.
- You are interested in policies with an investment component.
- You need financial security for beneficiaries regardless of when you pass away.
Consider Insurance If:
- You need affordable coverage for a specific term.
- You want flexibility to cover different types of risks.
- You are looking to cover temporary financial obligations.
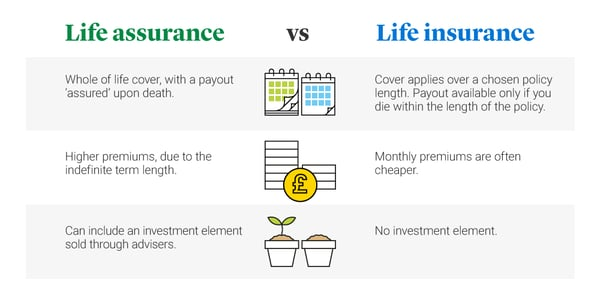
Understanding the key differences between assurance and insurance is essential for making informed financial decisions. Assurance offers lifetime coverage with a guaranteed payout, making it ideal for long-term security and estate planning. Insurance provides flexible, affordable coverage for specific terms and risks, suitable for temporary financial needs.
ALSO READ: Health Insurance For Families
By carefully considering your financial goals and needs, you can choose the right type of policy to provide peace of mind and financial protection for yourself and your loved ones. Remember to consult with financial advisors and read policy terms thoroughly to ensure you make the best choice for your unique situation.





